
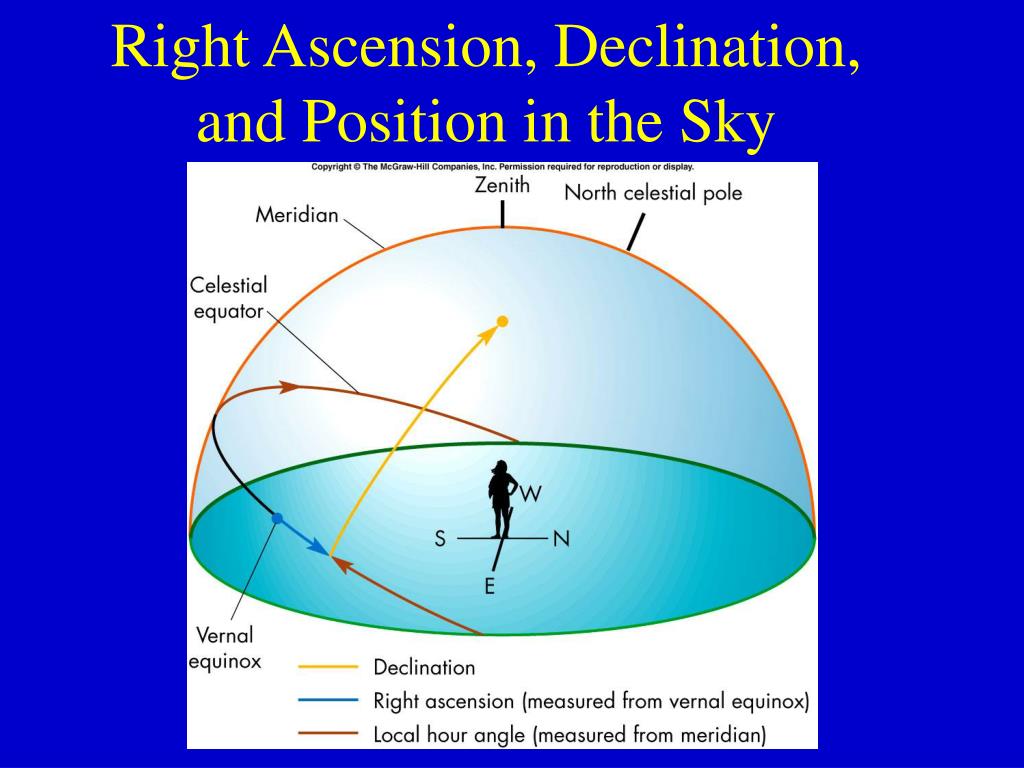
on the celestial equator) then at Earth's equator they are directly overhead (at zenith).Īny units of angular measure could have been chosen for right ascension, but it is customarily measured in hours ( h), minutes ( m), and seconds ( s), with 24 h being equivalent to a full circle. How high depends on their declination if 0° declination (i.e. On those dates at midnight, such objects will reach ("culminate" at) their highest point (their meridian). Īs seen from Earth (except at the poles), objects noted to have 12 h RA are longest visible (appear throughout the night) at the March equinox those with 0 h RA (apart from the sun) do so at the September equinox. Right ascension is measured continuously in a full circle from that alignment of Earth and Sun in space, that equinox, the measurement increasing towards the east. the First Point of Aries, which is the place on the celestial sphere where the Sun crosses the celestial equator from south to north at the March equinox and is currently located in the constellation Pisces. Right ascension is measured from the Sun at the March equinox i.e. Both right ascension and longitude measure an angle from a primary direction (a zero point) on an equator. Right ascension is the celestial equivalent of terrestrial longitude. Main article: Equatorial coordinate system It contrasts with oblique ascension, the point on the celestial equator that rises with any celestial object as seen from most latitudes on Earth, where the celestial equator intersects the horizon at an oblique angle. When paired with declination, these astronomical coordinates specify the location of a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system.Īn old term, right ascension ( Latin: ascensio recta) refers to the ascension, or the point on the celestial equator that rises with any celestial object as seen from Earth's equator, where the celestial equator intersects the horizon at a right angle. Right ascension (abbreviated RA symbol α) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the ( hour circle of the) point in question above the earth. Right ascension is measured eastward up to 24 h along the celestial equator from the primary direction.


The primary direction of the system is the March equinox, the ascending node of the ecliptic (red) on the celestial equator (blue). TT is independent of the irregular rotation of the Earth and its relation to the International Atomic Time (TAI*) is TT = TAI + 32.184 seconds.Right ascension and declination as seen on the inside of the celestial sphere. On the geoid, gravitational potential is the same everywhere and the gravitational force is perpendicular to the geoid. Terrestrial Time (TT) is the time standard used for precise calculation of astronomical events observed from the geoid.Declinations north of the celestial equator are positive, while those to the south are negative. "Dec" corresponds to the latitude on the celestial sphere, measured north or south of the celestial equator in degrees ( ° ), minutes ( ' ) and seconds ( " ). It is expressed in hours ( h ), minutes ( m ) and seconds ( s ), and if expressed in terms of angles, 1h=15°, 1m=15', 1s=15". "RA" corresponds to the longitude on the celestial sphere, measured eastwards along the celestial equator with respect to the zero hour of RA which passes through the two celestial poles and the vernal equinox point. Apparent right ascension (RA) and apparent declination (Dec) of the Sun are the astronomical coordinates of the Sun on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
